Europe’s Investments and Statistics Related to Sustainability

EU Fund Programs are important tools shaped to support sustainability, reduce environmental impacts, promote economic development, and ensure social justice. These fund programs contribute to the EU’s goals in this area by adopting sustainability principles and providing financial support to projects in various sectors.
The European Commission has taken important steps on the issue of environmental sustainability. For example, within the scope of the Horizon Europe program, support is being provided on topics such as the development of environmentally friendly technologies and the effective use of natural resources through research and innovation projects. The L’Instrument Financier pour l’Environnement (LIFE) Program, on the other hand, focuses on fulfilling the EU’s commitments in this area by aiming to implement environmental and climate policies. Additionally, the European Commission evaluates the environmental benefit impacts of projects and observes the sustainability contributions of accepted projects.
From an economic sustainability perspective, EU Funding Programs encourage businesses and industries to become greener and more efficient. These programs support economic growth by providing financing to entrepreneurs in various sectors, while also supporting projects on topics such as energy efficiency, renewable energy use, and the circular economy. It is important for projects to emphasize their sustainability contribution in order to receive EU funding. Today the European Commission wants to see the environmental impact in almost every call they publish.
The European Commission regularly invests in environmental sustainability to achieve the goals of the European Green Deal;
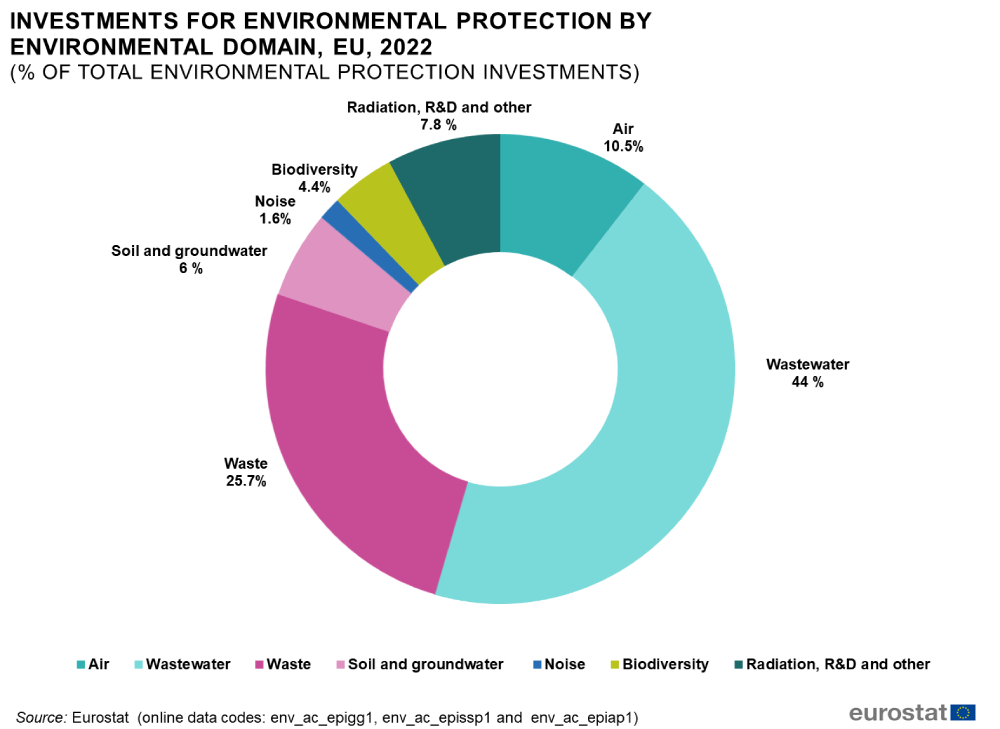
In 2022, the EU Commission invested 69 billion euros in environmental protection services. The majority of these investments went to wastewater and waste management services.
Of the total investments for environmental protection, 44% were allocated to wastewater management, 25.7% to waste management, 10.5% to air protection, 7.8% to protection against radiation, to environmental R&D and other environmental protection activities, including general environmental administration and education, 6% to soil and groundwater protection, 4.4% to biodiversity and landscape protection, and the remaining 1.6% to noise reduction.
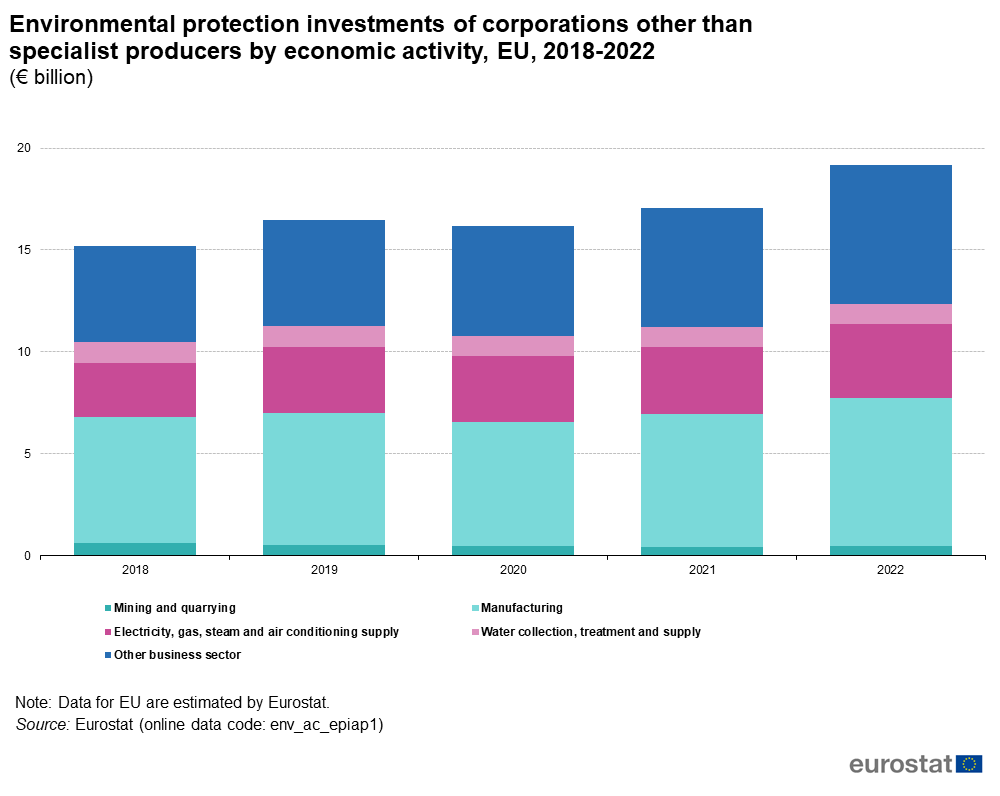
Source:
Recent Posts
- What is the CBAM Transition Period and First Phase Applications?
- Navigating Global Market Entry for Sustainable Startups
- 5 Questions About the Role of Corporate Academies in Corporate Transformation
- Agile Approach in Corporate Performance Management
- Life Cycle Analysis and Project Impact in European Union Fund Programs


